Centre of gravity:-
Center of gravity
Centre of gravity is a point where whole mass of the body lies, we can say its centre of whole mass, there is a formula to find centre of gravity of any given object.
Consider a object A whose centre of gravity lies at (x, y)
So to get (x, y)
Where
Xcm=Centre of mass at x
Ycm= Centre of mass at y
m1, m2, m3, are masses at x1,x2,x3 distance & y1,y2.y3 distance, it's a graphical representation of masses with respect to their distances.
- Why centre of gravity is important in robot designing?
- When robots are working they should not toppel, centre of gravity shows whether the object is stable or unstable.
- When robot is on inclination it's centre of gravity changes if you want it didn't topple make sure that centre of gravity always remain between the wheels.
- Some diagrams to explain where centre of gravity should lie in robots.
In this blog you will learn about Friction and its analysis, derivation of coefficient of friction.
Types of friction:
- Dry Friction
- Fluid Friction
Further dry friction is divided into two types:
- Static Friction
- Kinetic Friction
How to calculate value of friction?
How friction helps us in our daily life?
Daily life examples of friction.
— Friction is
the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and
material elements sliding against each other.
— A
resistance encountered when one body moves relative to another.
— A
force on objects or substances in contact with each other.
Note: - Forces of action reaction between contacting
surface act normal to the surface.
Examples of friction in our daily life
— Rubbing
both hands together to generate heat.
— Iron
being pushed across material
— Car
roaming on the streets.
— Turning
of bikes on curves.
— Skies
sliding on snow.
— Pulling
a trolley.
— Books
sliding.
— Walking
& many more…
Desired & Undesired friction forces
— Desired
friction forces are forces that help us in work.
Example: Friction help us in walking.
— Undesired
friction forces are forces that oppose our work, create resistance in our work.
It’s a loss of
energy.
Example, Friction between Gears
Fluid flow through pipes
Types of frictions
Dry Friction
Occurs between no lubricated surfaces of two solids
Fluid Friction
— Occurs
when adjacent layer in a fluid move at different velocities.
— Static
Friction
— When
applied force is less than or equal to the friction force & object doesn't
move is called static friction.
— F(r)≥F(a)
Where,
F(r) = friction force
F (a) = force applied
Kinetic Friction
— When
applied force is greater than friction force & object starts moving is
called kinetic friction.
- — F(r) <F(a)
Static
Friction
— Formula
F(r) = µs (N)
Where F(r) = Frictional Force
µs = Coefficient of static friction.
N = Normal force on the object.
Kinetic
Friction
— Formula
F(r) = µk (N)
Where, F(r) = Frictional force value.
µk = coefficient of kinetic friction
N = Normal force on object.
Coefficient
of friction (µ)
Object is in static Equllibrium.
F = F(r)
F(r) = µ mg cosα
F = mg sinα
Mgsinα = µ mgcosα
µ= mgsinα
/ mgcosα
µ= tanα
Tanα ≤ 1
µ ≤ 1
Friction
in Robotics,
- Robots on inclination slides back on track.
- For this problem friction should be increased in wheels, grips should be applied.
- Friction between gear is loss of energy implies to decrease in efficiency of robots.
- Friction must be reduced for reducing friction grease to be applied on gears.
- Friction between gears scrapes the gear teeth, and it destroys gear motors.
- For heavy work high torque motor to be used
These are basics of friction we will further learn about frictional analysis, point of application of friction force.
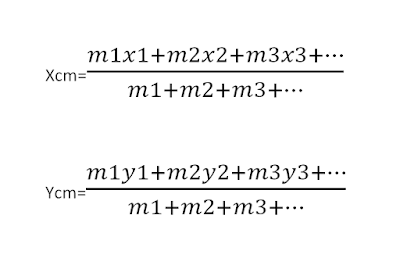







Comments